Drilling Fluids
Stabilizes Shales and Fluid Loss Control
Drilling Fluids
Drilling fluids, also referred to as drilling mud, are added to the wellbore to facilitate the drilling process by suspending cuttings, controlling pressure, stabilizing exposed rock, providing buoyancy, and cooling and lubricating. Drilling fluids are essential to drilling success, both maximizing recovery and minimizing the amount of time it takes to achieve first oil.
During drilling, cuttings are obviously created, but they do not usually pose a problem until drilling stops because a drill bit requires replacement or another problem. When this happens, and drilling fluids are not used, the cuttings then fill the hole again. Drilling fluids are used as a suspension tool to keep this from happening.
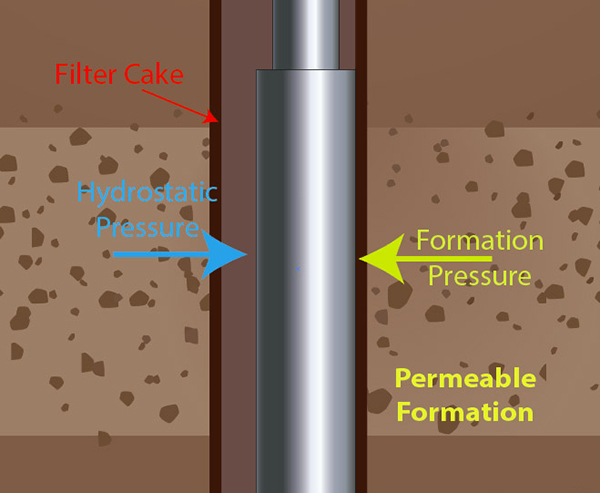
Drilling fluids also help to control pressure in a well by offsetting the pressure of the hydrocarbons and the rock formations. Weighing agents are added to the drilling fluids to increase its density and, therefore, its pressure on the walls of the well.
Another important function of drilling fluids is rock stabilization. Special additives are used to ensure that the drilling fluid is not absorbed by the rock formation in the well and that the pores of the rock formation are not clogged.
For many years, Gilsonite has been used in the oilfield as an additive in drilling fluids. Gilsonite, in various grades and formulations, has been used to combat borehole instability problems, provide lubricity, especially in highly deviated holes, and more recently as a bridging agent to combat differential pressure sticking and provide a law invasion coring fluid.
Drilling Fluids System Advantage
Provides Superior Shale Stabilization
Prevents Differential Sticking
Prevents Lost Circulation
Provides Well-Bore Strengthening Matrix
Use of Gilsonte in Fluid Loss Control
Gilsonite has been added to drilling fluids to give better stability of well walls, to lubricate the drill string in a well, to seal micro-fractures and thus prevent the formation of larger fractures and to decrease the loss of filtrate to formations at high temperatures.
The use of FLC in drilling fluid dispersions or mud, to coat the walls of well holes, is an old and well-established procedure. The purpose of the fluid is to stabilize the walls of the hole by forming a relatively thin but strongly adherent coating or cake on the walls. The coating must be able to withstand relatively high temperatures and it should be resistant to the passage of moisture or fluid there through.







